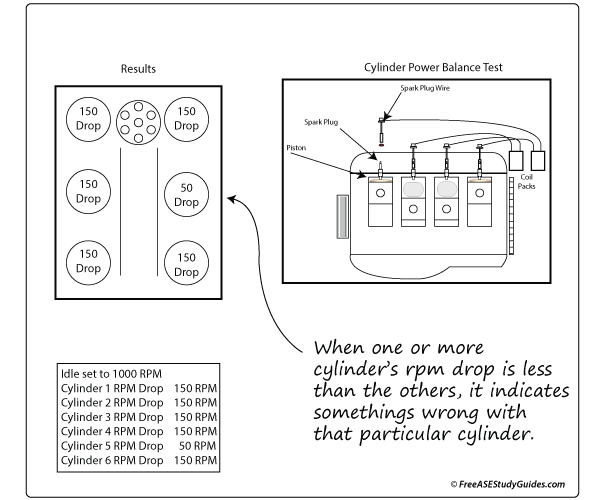
Cylinder Power Balance Test
A cylinder power balance test compares each cylinder's effectiveness with the others. Ignition, fuel delivery, and mechanical problems such as faulty valves or worn piston rings result in a weak cylinder. There may be one or more cylinders involved. For example, a faulty head gasket, cracked cylinder head, or block will cause an RPM drop on adjacent cylinders.
Disabling a cylinder by removing the plug boot from its sparkplug was standard for many years. Check with the manufacturer's specifications; a prolonged open in the secondary ignition system may cause damage to the coil or ignition module. In addition, raw fuel flowing into the catalytic converter causes it to overheat. Use a bidirectional scan tool. Sometimes, an O2 sensor must be disconnected so the computer will not compensate for the sudden change in conditions.
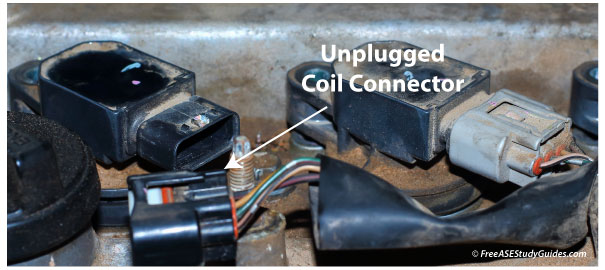
Notice the RPM drop as the cylinder is disabled. If it is inconsistent with the others, it indicates a problem with that cylinder. An engine analyzer tests each cylinder and then compares the results. It is easy to do the same with pencil and paper. An engine analyzer or dedicated tool is best for testing COP coil on plug ignition systems. Check with the manufacturer; there are many ways to cancel a cylinder, such as disconnecting the fuel injector's connector.