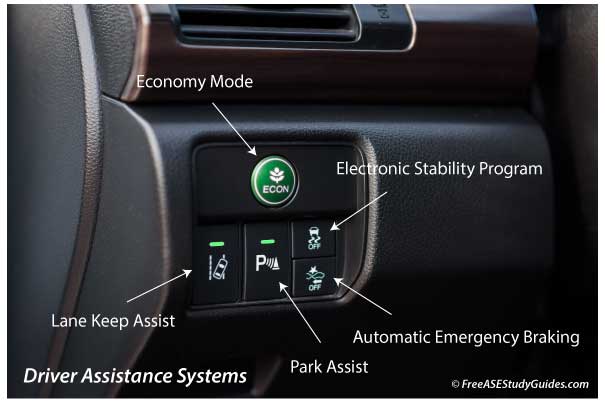
Lane Keep and Park Assistance
Automotive manufacturers install Advanced Driver Assistance Systems ADAS in their vehicles to improve safety and reduce accidents caused by human error. ADAS uses cameras, radar, and ultrasound with networked image-processing (Sensor Fusion) ECUs to sense and process the environment. The systems use the EPS electric power steering, electronic throttle, and ABS braking systems for active control.
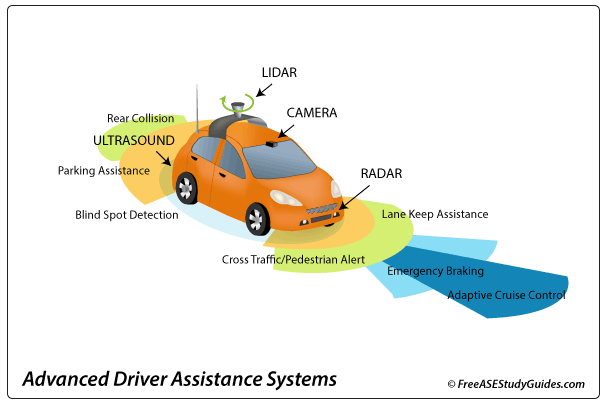
There are different levels (0-5) of driver assistance. Low-level systems (0) are passive and warn the driver, and high-level systems (5) are active and can completely automate driving. Lane departure warning systems warn the driver when the vehicle veers from its lane. Land-keeping assistance LKA systems warn the driver of lane departure and actively assist when the system senses drift or an undesired lane change.

The system uses vision-based cameras to follow the center and outer lane markings and the electric power steering, the ABS brake system, or both to keep the vehicle centered. Cameras can look in all directions and identify lane markings, stop signs, turn signals, and pedestrians. The LKA system is active and will assist and keep the vehicle in its lane if the driver does not make the corrections.
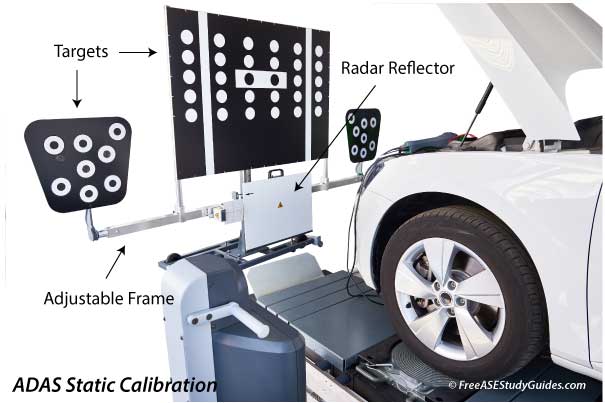
Not all roads have clear markings, and poor weather can affect the system. The camera lens should be kept clean from mud and road debris, and they can fall out of alignment from a collision or repair and need recalibration. Special equipment like an adjustable frame, targets, and scan tools with ADAS software may be required to calibrate ADAS sensors.
Park Assist
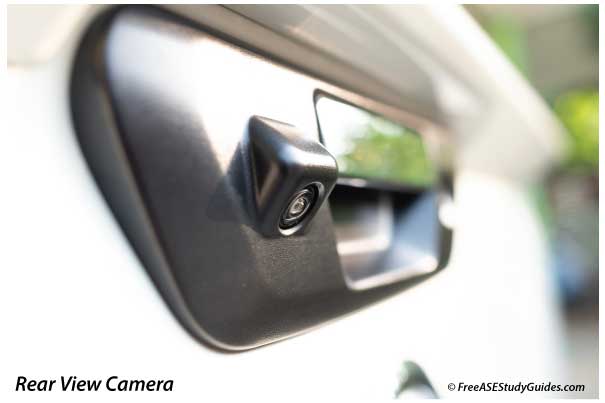

Parking Assistance relies on an ECU, a backup camera, and front and rear bumper sensors. This location exposes the sensors to dirt, debris, and damage. Remove and check the sensor plug and measure and compare the resistance measurements with OEM.

Park assist sensors are ultrasonic proximity sensors that measure short distances. A dirty or faulty sensor is a common problem resulting in fault codes and a parking system error message on the display. Cleaning the dirty sensor can restore the sensor's signal. On many models, the long holding of a button on the vehicle navigation or information center resets the system after cleaning the sensor.
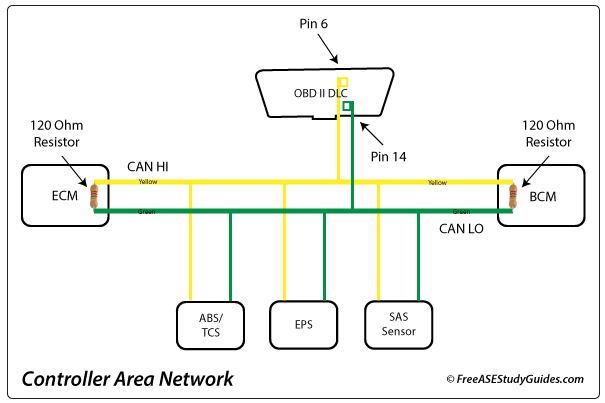
The automatic transmission, throttle control, electric power steering, and brake systems are involved in Park Assist. The Controller Area Network allows the different ECUs to communicate over a high-speed bus. Modern vehicles offer more features and can parallel and reverse park. Older systems focused on steering, leaving acceleration, and braking for the driver. Some modern park assist systems control everything: brakes, steering, and even finding a suitable parking spot for the driver.